Glass, a material that is all around us, plays a vital role in our daily lives. From the windows in our homes to the screens of our smartphones, glass is used in various applications. But have you ever wondered how glass is made from sand? It’s a fascinating process that involves transforming humble sand into a versatile and transparent material. Let’s explore the journey of sand to glass and discover the intricate steps involved in its production.
1. Gathering the Raw Materials
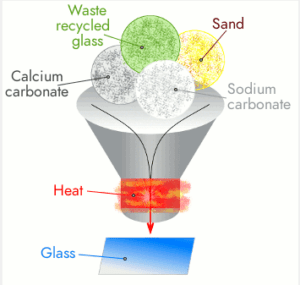
The primary ingredient in glass production is silica, which is derived from sand. Sand, composed primarily of silicon dioxide (SiO2), is found abundantly in nature. However, not all types of sand are suitable for making glass. The sand used in glassmaking is specially selected for its high silica content and low levels of impurities.
2. Preparing the Batch
Once the appropriate sand is obtained, it is mixed with other materials to form a batch. The batch consists of silica sand, along with fluxes and additives. Fluxes are substances that lower the melting point of silica, making it easier to work with. The most commonly used flux in glassmaking is soda ash (sodium carbonate). Additives may include lime (calcium oxide) for stabilization and various metal oxides to impart specific colors to the glass.
The proportions of these ingredients vary depending on the desired type of glass being produced. The batch is carefully measured and mixed to ensure a homogeneous mixture.
3. Melting the Batch
The mixed batch is then heated in a furnace to very high temperatures. The intense heat causes the batch materials to melt and fuse together, forming a molten glass. The temperature required for melting depends on the specific composition of the batch and the type of glass being produced, but it typically ranges between 1400°C and 1600°C (2550°F and 2910°F).
4. Shaping the Glass
Once the batch has melted into a viscous liquid, it is ready for shaping. There are several methods used to shape glass, depending on the desired end product. The most common methods are blowing, pressing, and casting.
- Glassblowing: In this ancient technique, a glassblower gathers molten glass on the end of a blowpipe and blows air into it. The glassblower shapes the glass by manipulating and blowing into the pipe, creating various forms such as bottles, vases, and drinking glasses.
- Pressing: In this method, the molten glass is poured into a mold and pressed into shape using a plunger. This technique is commonly used to produce items with intricate designs, such as glassware or decorative objects.
- Casting: Casting involves pouring the molten glass into a mold and allowing it to cool and solidify. This method is often used for producing thick glass objects or sculptures.
5. Annealing and Finishing
After the glass has been shaped, it undergoes a process called annealing. Annealing is a crucial step that involves slowly cooling the glass to relieve internal stresses and strengthen its structure. The glass is placed in a temperature-controlled chamber known as an annealing oven and gradually cooled over a period of several hours or even days, depending on the thickness and size of the glass.
Once the glass has been annealed, it may go through additional processes to achieve its final appearance. These processes can include cutting, polishing, grinding, and applying coatings to enhance its clarity or durability.
Recycling Glass
Glass is a highly recyclable material, and recycling plays a significant role in its sustainability. Recycling glass reduces the demand for new raw materials and requires less energy compared to manufacturing glass from scratch. Recycled glass, or cullet, can be melted down and mixed with virgin materials in the batch to produce new glass products.
Conclusion
The transformation of sand into glass is a complex and fascinating process. From the selection of the right sand to the precise mixing of ingredients, melting, shaping, and finishing, each step contributes to the creation of this versatile and transparent material that we rely on in countless aspects of our lives. Whether it’s a window pane, a decorative object, or a high-tech device, the journey of sand to glass highlights the remarkable ingenuity of humans and the endless possibilities offered by this ancient yet ever-evolving material.


